How Low-Impact Exercise Can Lead to a Healthier You
Wednesday,April 2, 2024Low-impact exercise offers several of the same benefits of high-intensity workouts, only without the stress and physical demands of […]
Your Diabetes Guide
Navigate your way through the complex world of diabetes with our guide. Wherever you are on your journey, we can help!

Am I at risk?

What is
diabetes?
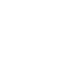
How do I
control it?

Learn your
lifestyle

Get
support
High-fat, low-carbohydrate diets may be best for people with diabetes, according to a small Linköping University study. Researchers enlisted 61 […]